Introduction
- ssldump is an SSL/TLS network protocol analyzer.
- It identifies TCP connections on the chosen network interface and attempts to interpret them as SSL/TLS traffic.
- When it identifies SSL/TLS traffic, it decodes the records and displays them in a textual form to stdout. If provided with the appropriate keying material, it will also decrypt the connections and display the application data traffic.
How To Open ' ssldump '
- To open ' ssldump ' goto --> BackTrack > Information Gathering > Network Analysis > SSL Analysis > ssldump
- See the below image for more help -
Output Format
Before using ssldump , understand the following points -
- All output is printed to standard out.
- ssldump prints an indication of every new TCP connection using a line like the following
New TCP connection #2:192.168.232.172(1232) <-> maa03s17-in-f24.le100.net(80)
- The host which send the first SYN is printed on the left and the host which responded is printed on the right.
- Ordinarily, this means that the SSL client will be printed on the left with the SSL server on the right.
- In this case we have a connection from 192.168.232.172(port 1232) to maa03s17-in-f24.le100.net(port 80). To allow the user to disentangle traffic from different connections, each connection is numbered. This is connection 2.
- The printout of each SSL record begins with a record line. This line contains the connection and record number, a timestamp, and the record type, as in the following:
2 3 0.2001 (0.0749) S>C Handshake Certificate
- This is record 3 on connection 2. The first timestamp is the time since the beginning of the connection. The second is the time since the previous record. Both are in seconds.
- The next field in the record line is the direction that the record was going. C>S indicates records transmitted from client to server and S>C indicates records transmitted from server to client. ssldump assumes that the host to transmit the first SYN is the SSL client (this is nearly always correct.
- The next field is the record type, one of Handshake, IAlert, ChangeCipherSpec, or application_data. Finally, ssldump may print record-specific data on the rest of the line. For Handshake records, it prints the handshake message. Thus, this record is a Certificate message.
- ssldump chooses certain record types for further decoding. These are the ones that have proven to be most useful for debugging: ClientHello - version, offered cipher suites, session idif provided)ServerHello - version, session_id, chosen cipher suite,
- compression method
- Alert - type and level (if obtainable)Fuller decoding of the various records can be obtained by using the -A , -d , -k and -p flags.
How to use ' ssldump '
- To use ssldump , we have to follow all the options associated to ssldump ,as we are now going to use .
- First we simlply run the ' ssldump ' on my interface(eth0) to check is it working or not , then afterwards we implement other options it .
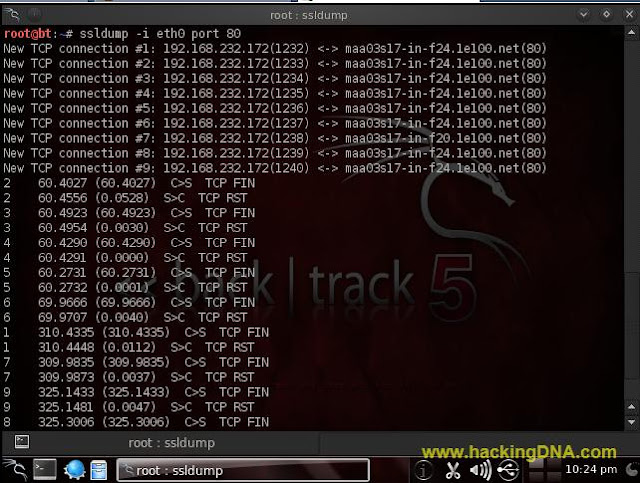
- Command Syntax : ssldump -i < interface > port < port no. >
- Command Used : ssldump -i eth0 port 80
- See the below image for the result -
- When some one on the interface opens any website on port 80(http), ssldump captures traffic.
- See the below image for more details -
HELP OPTION
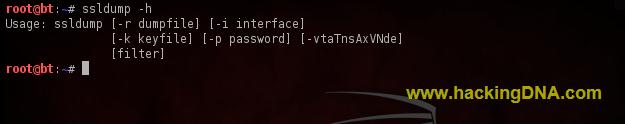
- To use ssldump help options , use the coammnd given below -
- Command Used : ssldump -h
- See the below image for more details -
-a option
-A Option |
- Display the application data traffic. This usually means decrypting it, but when -d is used ssldump will also decode application data traffic before the SSL session initiates.
- This allows you to see HTTPS CONNECT behavior as well as SMTP STARTTLS. As a side effect, since ssldump can't tell whether plaintext is traffic before the initiation of an SSL connection or just a regular TCP connection, this allows you to use ssldump to sniff any TCP connection.
- ssldump will automatically detect ASCII data and display it directly to the screen.
- non-ASCII data is displayed as hex dumps.
- See the below image for more details -
-e Options
- Print absolute timestamps instead of relative timestamps.
- See the below image for more details -
-H Option
- Print the full SSL packet header.
- See the below image for more details -
This is how we can use ' ssldump ' on BackTrack 5
More examples will be added soon





.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)

No comments:
Post a Comment