OPTIONS
- -f
- Force a zone transfer from an authoritative nameserver. dnswalk normally will look in its saved 'axfr' file for each domain and use that. (if it exists, and the serial number has not increased)
- -r
- Recursively descend sub-domains of the specified domain. Use with care.
- -a
- Turn on warning of duplicate A records. (see below)
- -d
- Print debugging and 'status' information to stderr. (Use only if redirecting stdout) See DIAGNOSTICS section.
- -m
- Perform checks only if the zone has been modified since the previous run.
- -F
- perform "fascist" checking. When checking an A record, compare the PTR name for each IP address with the forward name and report mismatches. (see below)
- -i
- Suppress check for invalid characters in a domain name. (see below)
- -l
- Perform "lame delegation" checking. For every NS record, check to see that the listed host is indeed returning authoritative answers for this domain.
- -D dir
- Use dir as the directory to use for saved zone transfer files. Default is '.'.
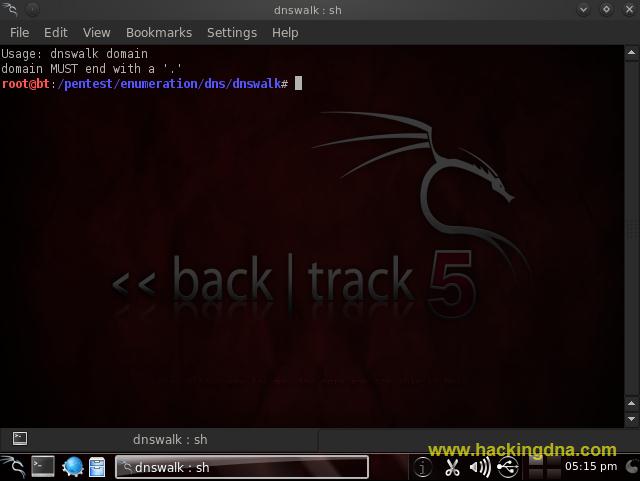
- How To Open dnswalk
- BackTrack > Information Gathering > Network Analysis > DNS Analysis > dnswalk
- See the below image for more details -
- EXAMPLE 1 : Help Options
- See the below image for more details -
EXAMPLE 2 : When Zone Transfer is Enabled
- Target Website -> listpk.com | Website Zone Transfer is enabled .
- See what happen when ZONE TRANSFER is enabled .
- See the below image for more details -
EXAMPLE 3: When Zone Transfer is disabled with -f option
- -f option force a zone transfer from an authoritative nameserver. dnswalk normally will look in its saved 'axfr' file for each domain and use that. (if it exists, and the serial number has not increased)
- The attempt FAILED and REFUSED by the server because by default these days zone transfers are set to disabled unless and until the admin enables it.
- See the below image for more details -
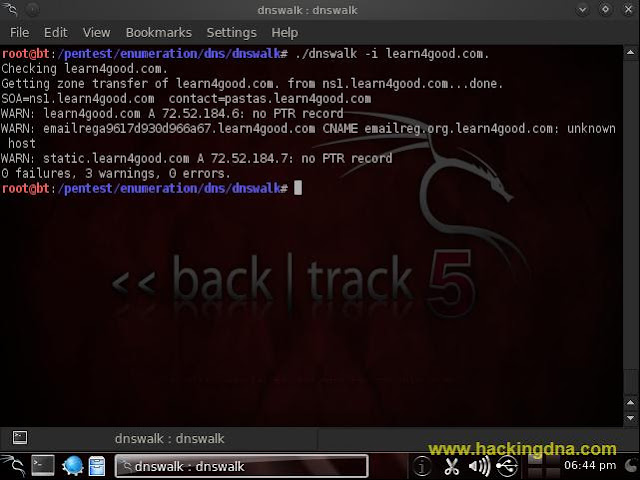
EXAMPLE 4 : dnswalk -i < domain >
- Suppress check for invalid characters in a domain name.
- See the below image for more deatils -
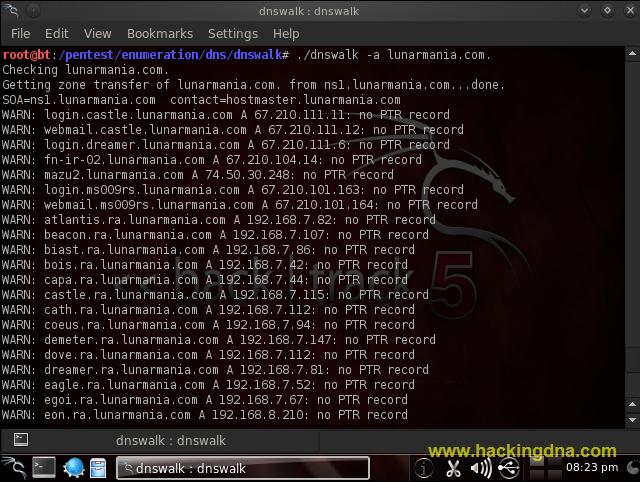
EXAMPLE 5 : dnswalk -a < domain >
- Turn on warning of duplicate A records. (see the below image )
- See below image for more details -
EXAMPLE 6 :./dnswalk -d < domain >
- Print debugging and 'status' information to stderr. (Use only if redirecting stdout) See DIAGNOSTICS section.
- See the below image for more details-
EXAMPLE 7 : ./dnswalk -m < domain >
- Perform checks only if the zone has been modified since the previous run.
- See the below image for more details -
EXAMPLE 8 : ./dnswalk -F < domain >
- This option perform "fascist" checking. When checking an A record, compare the PTR name for each IP address with the forward name and report mismatches. (see below) .
- See the below image for more details -
EXAMPLE 9 : ./dnswalk -rfiadmFl < domain >
- You can even use every options at once . As shown in the image below -
- See the below image for more details -
EXAMPLE 10 : ./dnswalk -rfiadmFl < domain >
- Save the result in dnslog.txt file .
- See the below image for more details -
THIS IS HOW WE CAN USE THIS TOOL .
ITS A GREAT DNS ANALYSIS TOOL .